What is CBD?
CBD (or Cannabidiol), is one of the most effective out of 110 cannabinoids found in hemp and cannabis leaves.
 |
| Hemp plants are rich with the powerful CBD element, helping to balance sleep, pain, emotions, immune system and other organism functions |
Cannabidiol molecules have existed in nature for millions of years, but were only discovered in 1940 by an American chemist, Roger Adams[1], while analysing the molecular structure of cannabis. He was the first to succeed in isolating the CBD molecule.
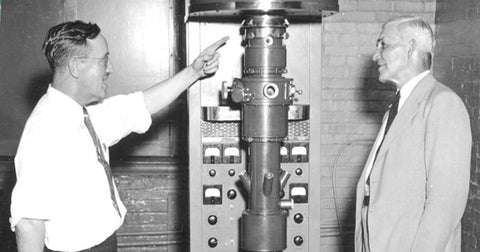 |
| The CBD pioneer Roger Adams (on the left), exploring the CBD isolation process in 1940 |
Since 1970, a number of studies by various scientists tried to clarify how CBD interacts with the human body.
The first official CBD experiment with people was conducted in 1978 by Jewish scientist Raphael Mechoulam[2] (he is now called “the father of CBD” and is still active in the cannabis medicine field).
 |
| Jewish scientist Dr. Raphael Mechoulam, who conducted the first experiments of CBD on human health in 1978. |
His team administered a daily dose of 300mg CBD isolate daily dose on a group of 8 people for 4 months and observed, how would that treat epilepsy.
The results were surprisingly positive. 4 of the subjects stopped having seizures alltogether, while 3 had a decrease in frequency (that was the main groundwork leading to creation of anti-epilepsy drugs called „Epidiolex“ 30 years later).
The study was met controversially (as were most topics related to cannabis) but it attracted wide public curiosity for the CBD ingredient. As a result, it also initiated a chain of new studies.
A 1988 study by American scientist W. A. Devane showed[3] that our neural and immune systems are full of so called endocannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2, which react to both endocannabinoids (the ones produced by our body) and phytocannabinoids (the ones produced by plants).
The psychoactive cannabis element THC binds to both receptors, making people dizzy and anxious.
CBD, meanwhile, works in a different way. It does not bind to neither, but instead helps our inner cannabinoids (endocannabinoids) to become more effective.
Endocannabinoids are the 24/7 workforce keeping long-term balance in our neuro/immune systems, which sometimes react too sensitively to the negative influences in our lives — disease, injury, stress, bad people, to name a few.
Endocannabinoids work well enough under normal conditions, but in some extreme situations they fail to keep the balance.
Therefore, CBD is a great peacemaker when things get out of hand.
CBD food supplements are mostly valued for bringing daily physical and mental functions or reactions, such as sleep, pain, emotions, immune system, back into balance.
Even though there are only a few officially approved CBD drugs and all of them are very expensive, 2019 surveys showed that 7% of the US population already use CBD on a regular basis, mostly as food supplements or cosmetics.
Due to its rapidly increasing popularity, Cannabidiol can now be found in all sorts of forms — oils, capsules, creams, beverages, coffee, gummies and many others, so everyone can pick his/her preferred formula.
Oils and capsules are typically made from hemp leaf extract, rich with a full or broad spectrum of cannabinoids (except THC), terpenes and flavonoids. Meanwhile, other CBD product types usually contain isolated CBD crystals.
It is important to mention that CBD is neither addictive nor intoxicating, so it is safe to use. This fact was confirmed by the World Health Organization in 2018.[4]
[1] https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ja01858a058
[2] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/351429/
[3] http://molpharm.aspetjournals.org/content/34/5/605.long
[4] https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/cannabidiol-(compound-of-cannabis)











